Instruments for water purging utilizing a layer-based process, like ultrafiltration and microfiltration, include size-strainer filtration that eliminates little solids from the water.
Click on this howtat.com
related terms:
Chitosan EcosystemNanotechnologyBiodiversity Drinking WaterNano Materials Water Treatment Sewage Nanoparticles Cellulose
see all points
Add to Mendeley Download as PDF
set alert
about this page
Nanostructured layers for microbiological sanitization of drinking water
You should know all about how to add money to paypal
1. Presentation
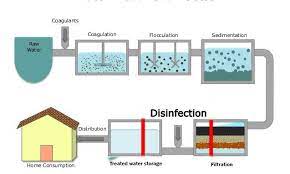
Water purging for human utilization purposes includes the evacuation of different toxins such as synthetic compounds (i.e., poisons, poisonous metals), organic impurities (green growth, microorganisms, organisms, parasites, infections), suspended solids, and gases.
A few strategies are utilized in the water sanitization process, including (1) actual cycles, like filtration, sedimentation, or refining; (2) natural cycles, for example, sand channels, enacted carbon; (3) Chemical cycles, like flocculation, chlorination, the utilization of bright light.
Concerning the actual methodologies utilized in water purging, they vary in the degree to which the cycles are based. For instance, filtration depends on isolating solids from fluids by adding a permeable medium (channel), which holds strong particles and permits fluids to go through to the opposite side. Then again, the sedimentation approach utilizes the power of gravity to decide the strong to be stored at the lower part of a cylinder containing debased water, though refining includes the transformation of fluid (water) into the fume stage, the interaction which depends on the development of mixtures. on the distinction in unpredictability.
Slow sand channels address an illustration of organic methodologies utilized in water sanitization, and that implies utilizing tubes 1-2 m profound loaded up with sand, which hold the pollutions present in the sifted water. Initiated carbon (charcoal), one more utilized approach, is a fine-grained carbon with a high surface region and high-level adsorption properties.
In logical terms, flocculation is a cycle wherein colloids in suspension become temperamental after an explaining specialist is added; concerning the water cleansing cycle, the flocculation peculiarity can allude to the shakiness and coagulation of pollutants present in the water. Water supply treatment as a rule includes chlorination of water and incorporates chlorine or hypochlorite to kill microorganisms and forestall the spread of waterborne infections.
The utilization of electromagnetic light, particularly short frequencies (in the bright reach), is usually utilized in the sanitization, because of the way that it makes holes in the nucleic corrosive construction of microorganisms that handicap their cell capabilities. does. This technique is many times utilized in water purging.
This part basically centers around the most usually researched actual strategies including the filtration cycle. Contrasted and different strategies utilized in water treatment, layer water filtration presents a few benefits, for example, (1) coherence of activity; (2) It doesn’t need the utilization of any synthetics; (3) it doesn’t demonstrate high energy utilization; (4) the potential for increasing, coordinating/incorporating different cycles, and the potential for robotization (Street et al., 2014).
There are a few boundaries that influence the properties and productivity of films utilized in water filtration: (1) the size of the layer pores/size of the toxin atoms/particles; (2) the positive/negative charge of the layer surface, separately, the extremity of the pollutant particles; and (3) the adsorption limit of the film surface (Street et al., 2014).
Contingent upon the pore size of the channel (film) utilized, pollutants with various sizes can be eliminated and better cleaning can be accomplished while lessening the pore size; Thus, the techniques accessible are: (1) microfiltration (pore size roughly 0.1 µm), which eliminates microbes and suspended solids in water; (2) ultrafiltration (pore size around 0.01 µm), which eliminates infection notwithstanding microfiltration; (3) nanofiltration (pore size around 0.001 µm), which eliminates most natural particles and a few polyvalent particles (divalent particles from hard water); and (4) switch assimilation (pore size around 0.0001 µm), which eliminates every natural particle and minerals in the water, coming about in ultrapure water (Fig. 12.1).
Figure 12.1. Various kinds of films are based on pores and their filtration standards.
While breaking down the properties of these sorts of layers, obviously those with little pores are generally gainful. Notwithstanding, for cost-productivity purposes, these separating strategies can be utilized to get consumable water,
The advancement in water refinement has been for the most part adopted by the logical headway made in the distinguishing proof of microorganisms and different pollutants in water, the presentation of new guidelines with respect to water quality, yet additionally the improvement of materials science, brilliant materials, and nanomaterials. Today, there are numerous instances of business films for water purging; nonetheless, there is as yet a long-lasting requirement for development in regards to their properties, for example, (1) antifouling properties; (2) compound soundness; (3) mechanical strength; and (4) warm dependability.
Depending on their structure and chemical composition, membranes can also be grouped as (1) isotropic, having uniform physical nature and chemical composition in cross-section; and (2) anisotropic, which are nonuniform in cross-section.